Red cell autoagglutination is the process whereby red cells clump together forming aggregates. This is seen in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, cold agglutinin disease and Infection with Mycoplasma Pneumonia or Infectious mononucleosis. Also during COVID-19 disease or vaccination?

Autoagglutination represents clumping of an individual’s red blood cells (RBCs or erythrocytes) by his or her own serum due to the RBCs being coated on their surface by antibodies.

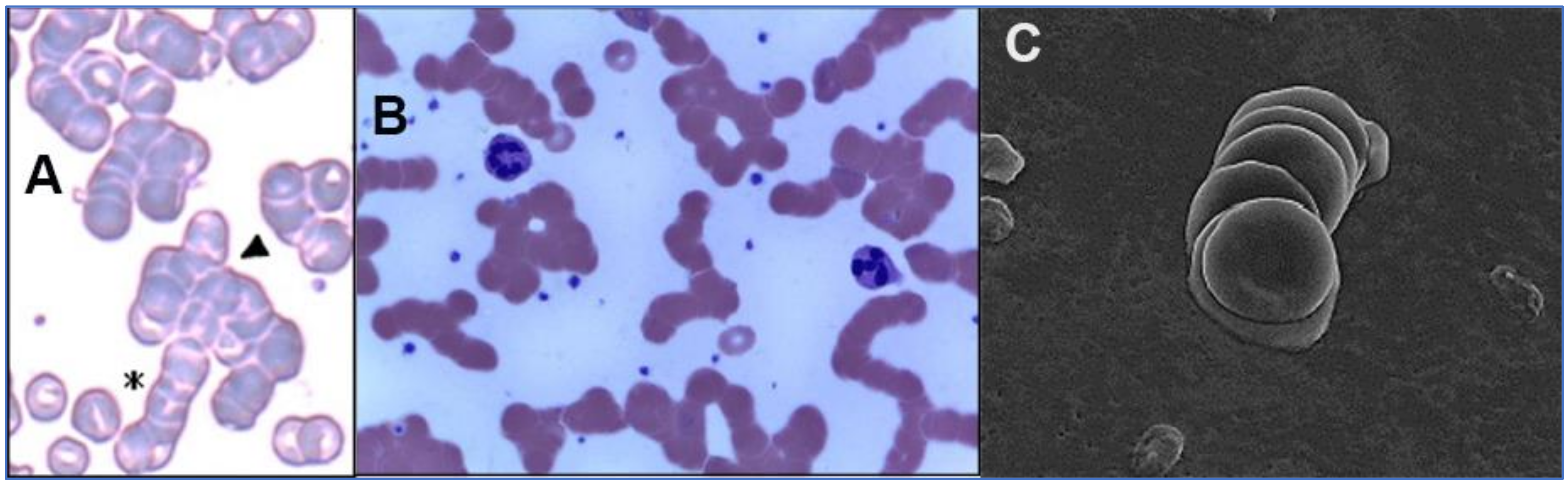
Autoagglutination vs rouleaux formation

RBC aggregation in serum 2012

- Rouleaux formation:
"stacking" of red blood cells (A) occurs in the presence of increased amounts of fibrinogen, immunoglobulin or acute phase reactants in the serum. Normal red cell membranes are negatively charged and red cells will normally "repel" one another. In the presence of positively charged proteins, the red cells may be brought together in these stacks, known as rouleaux. Because the stacks of red cells have a decreased surface to volume ratio, they are "denser" and will sink more rapidly if placed in a long column. This rate of "sinking" is known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and is an indirect measure of rouleaux formation. Conditions that increase the ESR include infection, inflammation and malignancy (since they are associated with increase in acute phase reactants), multiple myeloma (because of elevated immunoglobulin in the serum) and anemia (decrease in the viscosity of blood). Conditions that decrease the ESR include polycythemia (because of the increased viscosity of the blood and the presence of abnormally shaped red blood cells (sickle cells e.g. sediment more slowly because of their abnormal shape)

Cold Agglutinin Disease

Polytrauma in a geriatric patient resulting in reactivation of cytomegalovirus infection and secondary cold agglutinin disease-induced haemolytic anaemia, 2020
SARS-Cov2
red blood cells clumps and sars
A Deadly Embrace: Hemagglutination Mediated by SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein at Its 22 N-Glycosylation Sites, Red Blood Cell Surface Sialoglycoproteins, and Antibody, 2022